One of the problems of Android application support is to deofuscate or retrace stack traces obtained from an obfuscated release build. To figure out how to deobfuscate a stack trace, you need to understand how the obfuscation actually works. The standard way of obfuscation in Android development is done using tools such as the ProGuard. That’s what the official documentation says
The ProGuard tool shrinks, optimizesstatic innerand obfuscates your code by removing unused code and renaming classes, fields, and methods with semantically obscure names.
Well, looks good. Let’s try it. I will create a new project with Android Studio and add the following options to build.gradle file to obfuscate debug builds:
buildTypes {
debug {
minifyEnabled true
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
Let’s throw an Exception in the onCreate method of MainActivity class:
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
throw new RuntimeException("Stack deobfuscation example exception");
}
After running you will get something like:
Caused by: java.lang.RuntimeException: Stack deobfuscation example exception
at com.druk.myapplication.MainActivity.onCreate(Unknown Source)
at android.app.Activity.performCreate(Activity.java:6162)
at android.app.Instrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(Instrumentation.java:1107)
at android.app.ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2370)
at android.app.ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2477)
at android.app.ActivityThread.-wrap11(ActivityThread.java)
at android.app.ActivityThread$H.handleMessage(ActivityThread.java:1345)
at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:102)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:148)
at android.app.ActivityThread.main(ActivityThread.java:5415)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Native Method)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(ZygoteInit.java:725)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:615)
Why the MainActivity is still the MainActivity even after the obfuscation? The thing is that ProGuard uses default rules of Android projects obfuscation from the SDK in addition to the configuration file proguard-rules.pro in our catalog. And those default rules weaken the obfuscation of Activity's inheritors. The documentation contains the following guidelines for Android projects:
-keep public class * extends android.app.Activity
-keep public class * extends android.app.Application
-keep public class * extends android.app.Service
-keep public class * extends android.content.BroadcastReceiver
-keep public class * extends android.content.ContentProvider
By default ProGuard will keep names for all inheritors of android.app.Activity. Ok, I created an inner static class to avoid this rule.
private static class CrashHelper{
public static void crash(){
throw new RuntimeException("Stack deobfuscation example exception");
}
}
Now when I call method crash from onCreate I got:
Caused by: java.lang.RuntimeException: Stack deobfuscation example exception
at com.druk.myapplication.a.b(Unknown Source)
at com.druk.myapplication.a.a(Unknown Source)
at com.druk.myapplication.MainActivity.onCreate(Unknown Source)
at android.app.Activity.performCreate(Activity.java:6162)
at android.app.Instrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(Instrumentation.java:1107)
at android.app.ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2370)
at android.app.ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2477)
at android.app.ActivityThread.-wrap11(ActivityThread.java)
at android.app.ActivityThread$H.handleMessage(ActivityThread.java:1345)
at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:102)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:148)
at android.app.ActivityThread.main(ActivityThread.java:5415)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Native Method)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(ZygoteInit.java:725)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:615)
It’s exactly what we are looking for: the exception was thrown in method b of class a that was called from method ‘a’.
For deobfuscation we needed file mapping.txt from build. In my case path ro the file was app/build/outputs/mapping/debug/mapping.txt. Next you need to run script retrace.sh from ANDROID_HOME/tools/proguard/bin or run GUI utilits called ProguadGUI from ANDROID_HOME/tools/proguard/lib/proguardgui.jar. I used GUI utils and got the following:
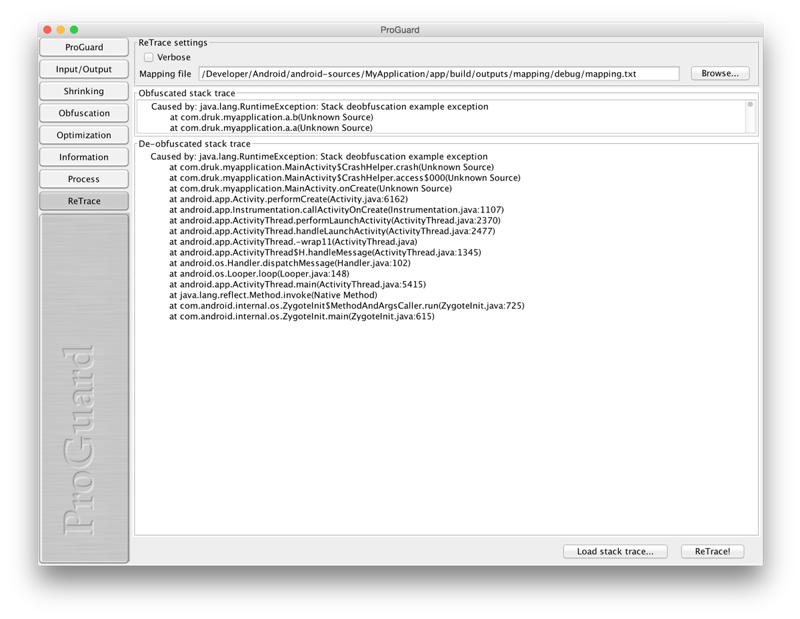
Caused by: java.lang.RuntimeException: Stack deobfuscation example exception
at com.druk.myapplication.MainActivity$CrashHelper.crash(Unknown Source)
at com.druk.myapplication.MainActivity$CrashHelper.access$000(Unknown Source)
at com.druk.myapplication.MainActivity.onCreate(Unknown Source)
at android.app.Activity.performCreate(Activity.java:6162)
at android.app.Instrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(Instrumentation.java:1107)
at android.app.ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2370)
at android.app.ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2477)
at android.app.ActivityThread.-wrap11(ActivityThread.java)
at android.app.ActivityThread$H.handleMessage(ActivityThread.java:1345)
at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:102)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:148)
at android.app.ActivityThread.main(ActivityThread.java:5415)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Native Method)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(ZygoteInit.java:725)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:615)
One more thing, we need numbers of lines in a file where the crash occurred instead of current Unknown Source. According to official docs for that you should add next lines to ProGuard properties:
-printmapping out.map
-keepattributes SourceFile,LineNumberTable
-renamesourcefileattribute SourceFile
The first rule is already in Android project by default, we will skip it. The second rule will switch on saving of source filename and table of line numbers. But the most interesting is the third one that will change all filenames to Source file. It’s critical for languages like Java where filenames are usually the same to class name. Also, it will hide relations between inner and outer classes.
After updating proguard file I got:
Caused by: java.lang.RuntimeException: Stack deobfuscation example exception
at com.druk.myapplication.a.b(SourceFile:42)
at com.druk.myapplication.a.a(SourceFile:40)
at com.druk.myapplication.MainActivity.onCreate(SourceFile:15)
at android.app.Activity.performCreate(Activity.java:6162)
at android.app.Instrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(Instrumentation.java:1107)
at android.app.ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2370)
at android.app.ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2477)
at android.app.ActivityThread.-wrap11(ActivityThread.java)
at android.app.ActivityThread$H.handleMessage(ActivityThread.java:1345)
at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:102)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:148)
at android.app.ActivityThread.main(ActivityThread.java:5415)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Native Method)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(ZygoteInit.java:725)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:615)
And after deobfuscation:
Caused by: java.lang.RuntimeException: Stack deobfuscation example exception
at com.druk.myapplication.MainActivity$CrashHelper.crash(SourceFile:42)
at com.druk.myapplication.MainActivity$CrashHelper.access$000(SourceFile:40)
at com.druk.myapplication.MainActivity.onCreate(SourceFile:15)
at android.app.Activity.performCreate(Activity.java:6162)
at android.app.Instrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(Instrumentation.java:1107)
at android.app.ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2370)
at android.app.ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2477)
at android.app.ActivityThread.-wrap11(ActivityThread.java)
at android.app.ActivityThread$H.handleMessage(ActivityThread.java:1345)
at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:102)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:148)
at android.app.ActivityThread.main(ActivityThread.java:5415)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Native Method)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(ZygoteInit.java:725)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:615)
To summarize, I would strongly recommend you to keep all mapping files for your release builds to be able to deobfuscate stack traces from crash logs. The best practice is building releases on your CI server with saving apk and mapping file with tags of releases. In this case, you will always know where you can find a mapping file for you release build. Also, there are a lot of services that provide automatic deobfuscation of stack traces such as Fabric or Google Play Developer Console. But keep in mind that you provide your mapping file to a 3-rd party service, and they can deobfuscate your builds and get all the source code.
I’m Andrew. Here I write about programming for mobile platforms
I am also the creator of developer tools such as LM Playground, Swift Android Toolchain and Bonjour Browser. If you find my tools and insights valuable, consider supporting my work on buymeacoffee.